Grumman/Butkus Associates has released Part 2 of the results of its 2014 Hospital Energy and Water Benchmarking Survey, focusing on water/sewer costs, carbon footprint, and costs-per-bed. To download this report, click here.
Part 1, covering fossil fuel and electricity usage trends, was released on March 6.
G/BA’s Hospital Benchmarking Survey, a no-cost resource, was initiated in 1995. Hospitals are invited to participate without charge by submitting responses to a short list of questions regarding their usage of electricity, natural gas, oil, purchased steam, purchased chilled water, and domestic water/sewer. This year’s information, covering usage patterns in calendar year 2013, was provided by a total of 102 hospitals located in Illinois (54), Wisconsin (29), Michigan (7), Minnesota (4), Indiana (3), and several other states.
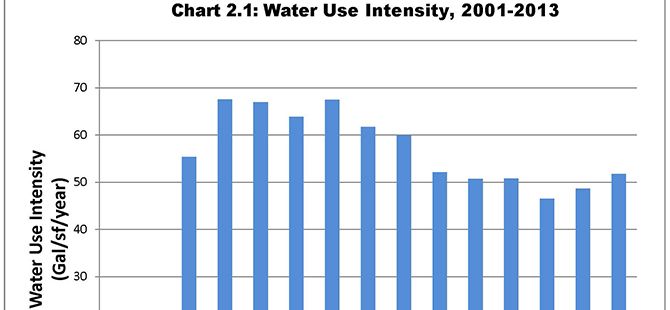
Although water and sewer costs are considerably less than those for electricity and natural gas, many parts of the country are experiencing price hikes, and there are pressing new concerns about water supplies and quality. Since 2001, when G/BA first started tracking water and sewer data, hospital usage of these resources has steadily declined.
“This downward trend reflects a movement to eliminate city-water-cooled equipment, as well as the use of low-flow and occupancy-based plumbing fixtures,” says G/BA Chairman Dan Doyle. “Water usage is an emerging issue. There is still much room for improvement in healthcare facilities.”
Our analysis of trends in carbon footprint since 1999 reveals that most hospitals have remained at an average usage intensity figure near 60 pounds/sf/year for well over a decade. “We do see a slight downward trend, due in part to increased reliance on electricity instead of fossil fuel,” says Doyle. “But we can and must do much better.”
The Part 2 report also contains costs-per-bed data, indicating an average annual outlay for all utilities (excluding water) of $9,000 per staffed bed for respondents from all states that included bed counts. Water costs averaged $1,050 per staffed bed.
Finally, our Part 2 report provides links to other benchmarking resources, and a comparison of G/BA’s stats with ENERGY STAR hospital stats.
For information about participating in the 2015 survey (compiling data from calendar year 2014), as well as download links to all the charts from the 2014 survey, visit our website’s HES page.